Plants in a Maze
As educators, we’re always on the lookout for hands-on learning activities that can capture our students’ curiosity about the natural world.
This experiment involves creating a small-scale “plant maze” using simple materials like cardboard and a shoebox. By guiding students through the setup and observation of this hands-on activity, you can help them delve into the wonders of how plants respond to light, obstacles, and other environmental factors as they strive to grow and thrive. This experiment is just one of the many exciting ways to integrate a plant growth unit into your elementary science curriculum.
Materials:
- A shoe box or cardboard box with a lid
- Cardboard strips
- Craft knife or scissors
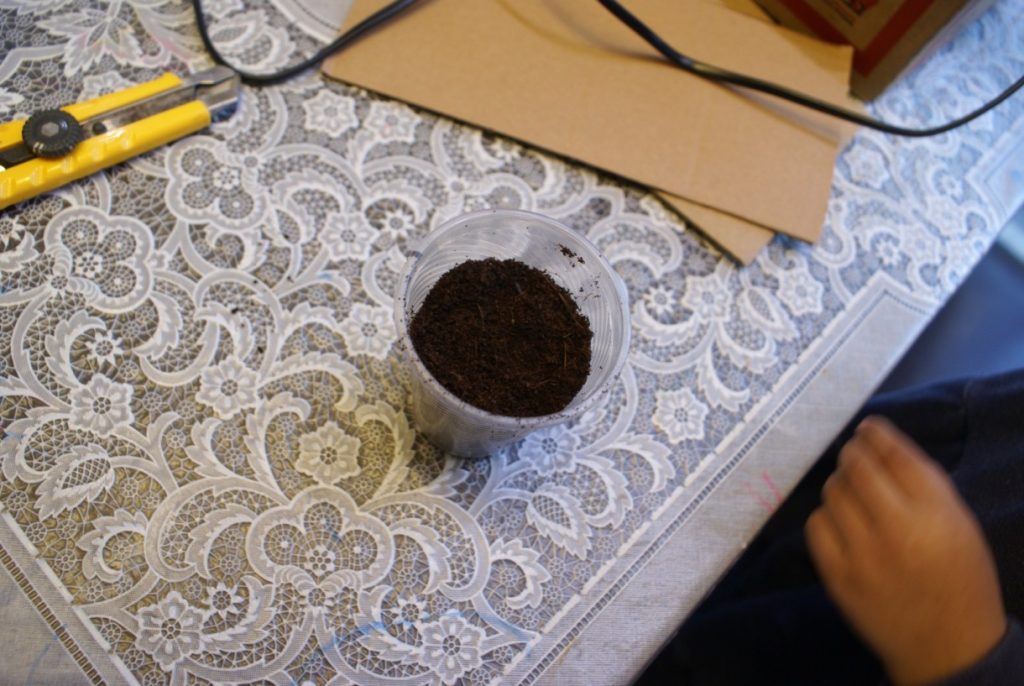
- Cup
- Soil
- Seeds
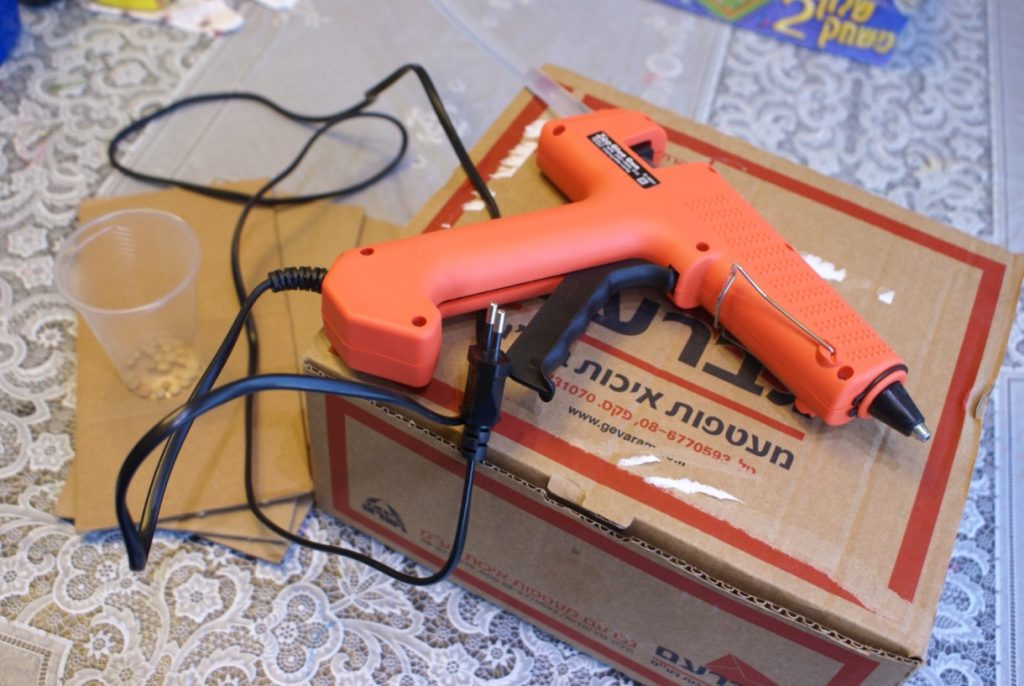
- Hot glue gun
What to do?
- Fill the cup with soil and plant 5-6 seeds.
- Place the box upright and cut a hole of about 3×3 cm in the top.
- Place the cup in the bottom of the box, measure about 5 cm above the cup, and glue a cardboard strip about 2/3 the width of the box, so that it blocks the plant from growing straight up.
- Measure about 10 cm above the cardboard strip and glue another cardboard strip, this time on the opposite side of the box, also about 2/3 the width.
- You can glue 2-4 strips.
- Water the seeds.
- Close the box and place it in a sunny spot.
- Every 2-3 days, open, check the plants growth and water it
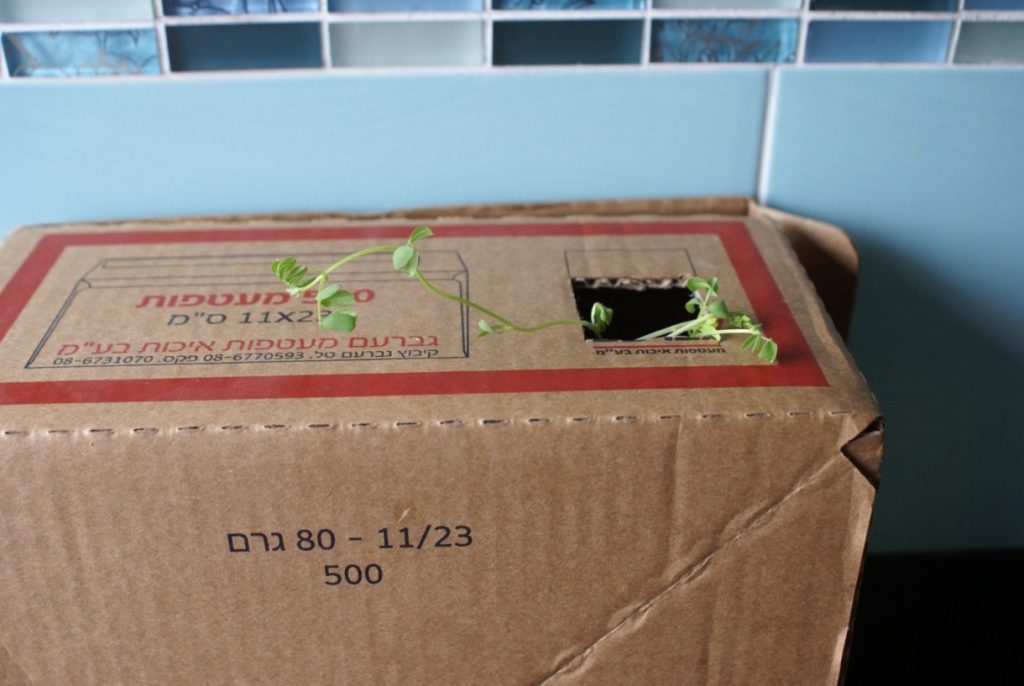
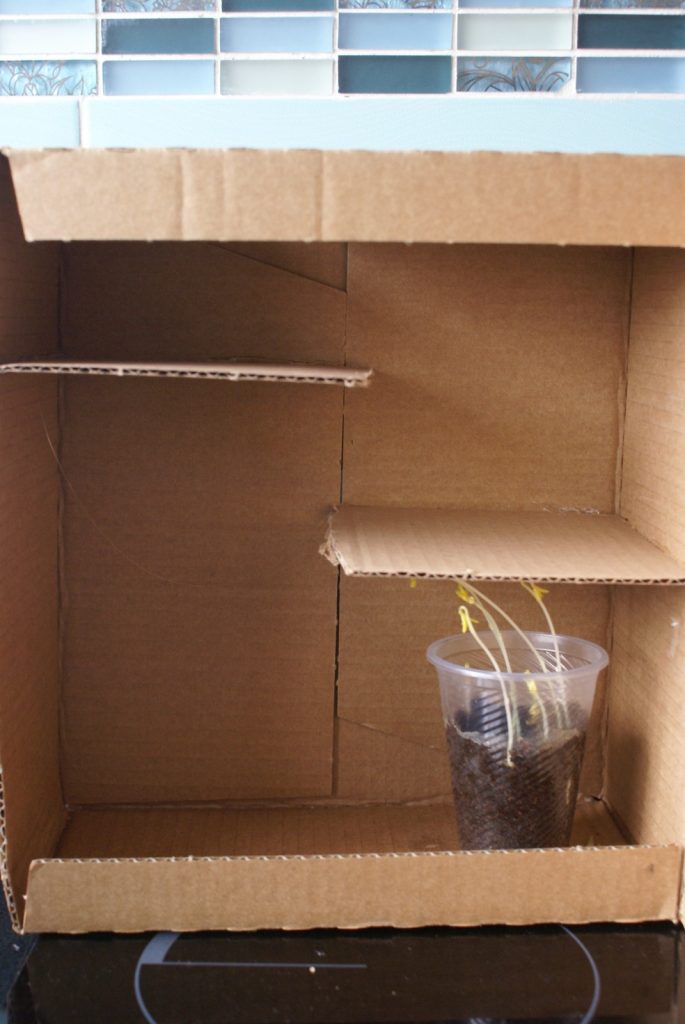







How does this happen?
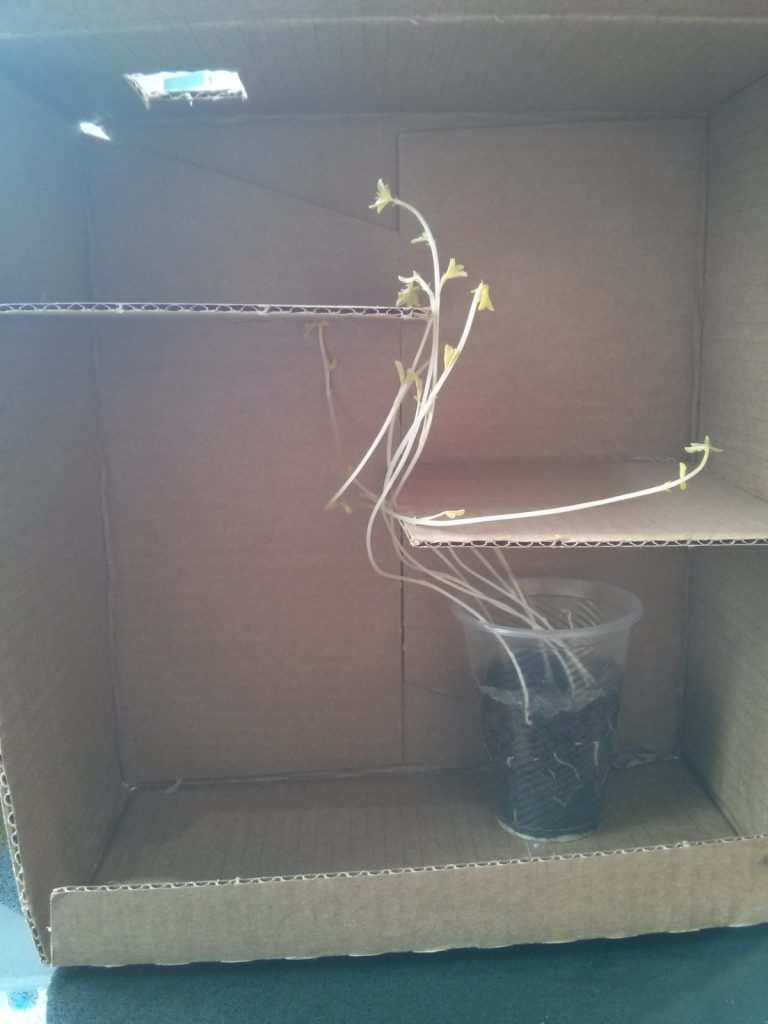
The seedling will start to grow towards the light and navigate its way through the maze until it reaches the opening in the box.
Why? Plants always seek light, as they need sunlight for photosynthesis and to produce the energy that fuels their growth.
The light enters the maze through the hole in the top of the box, and the plants will grow towards the light. This effect is called phototropism. When light shines on one side of a seedling, it grows more on that side, causing it to bend towards the light. This is also why potted plants on a windowsill often grow crooked, leaning towards the window.
During the observation, you will see that the leaves growing inside the box are pale, a very light greenish-yellow, since these plants are not exposed to direct sunlight and do not produce chlorophyll. Once the leaves emerge from the box, they will be green.
Additionally, the stem inside the box will have little or no leaves. Plants that grow without light or with very little light are called etiolated. They are pale in color and elongated, as they are trying to reach a light source before their food reserves in the seed are depleted. Their leaves are very small (or nonexistent) in order to conserve the little energy the plant has until it can reach the light and start producing its own food (the process of photosynthesis). Without sunlight, the plant will not produce chlorophyll, and without chlorophyll, photosynthesis cannot occur.
Looking for more science experiments about plant growth? Read my blog post:
Hands on Plant growth experiments.
We’d love to showcase your creativity!
Share pictures of your experiments with us, and together, we can inspire young scientists everywhere!